Arthrogram
In our Humble and Houston radiology facilities, we perform several forms of diagnostic imaging. When closer observation of a joint is necessary, arthrography may be the most appropriate type of exam.
What Is an Arthrogram?
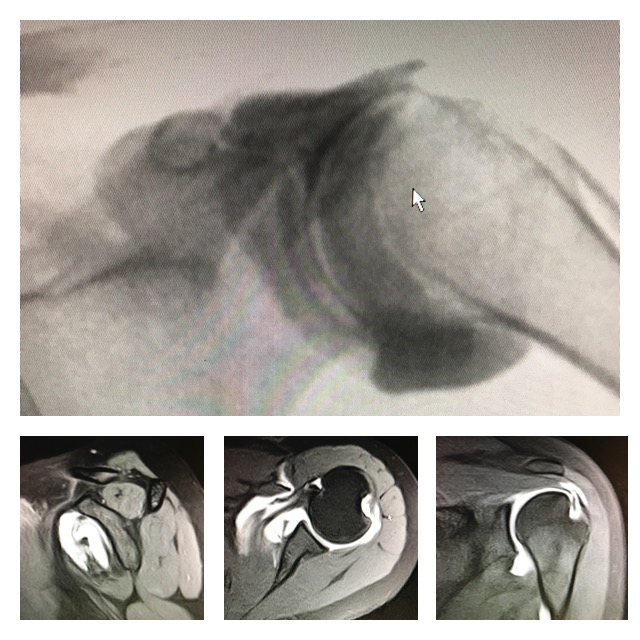
An arthrogram is a method of medical imaging in which we observe a joint through live X-Ray “Flouroscopy”. Imaging involves contrast media that facilitates the examination of structures that may not be accurately portrayed on a standard x-ray.
Reasons for an Arthography
Arthrograms help physicians understand the underlying cause of joint pain. Some of the common uses of an Arthrogram include:
- Identify disease, deterioration, or tears in cartilage, ligaments, bones, or the capsule of a joint.
- Observe the rotator cuff in the shoulder for damage such as a tear.
- Evaluation for fluid-filled cysts or other abnormal growths.
- Confirmation of proper needle placement for joint fluid analysis, or prior to injection therapy for joint pain.
What Areas May Be Observed Using Arthrography?
An arthrogram may observe the joint structure of the:
- Shoulder
- Elbow
- Wrist
- Hip
- Knee
- Ankle
Arthrogram Benefits
When joint space is injected with contrast medium, the quality of imaging improves. Contrast enables us to visualize finite details that may otherwise be too discreet to observe. For example, the use of contrast dye can show details such as:
- The location and degree of instability in a joint.
- A tear in cartilage tissue in the rim of the hip joint or the labrum in the hip.
- Tears in the small ligaments in the wrist.
These are just a few examples of situations for which arthrogram with contrast media can be advantageous.
Arthrogram Procedure
We use contrast material for Arthrograms in order to project a clear visual image of the joint structure in real time.
To complete the Arthrogram:
- The patient sits or lies down on an exam table.
- The doctor cleans the patient’s skin and drapes it with a sterile cloth
- We administer a local anesthetic to numb the joint area.
- The doctor introduces a dye into the joint structure.
- We may ask the patient to move the joint in order to disperse contrast material.
- The doctor then holds the joint very still while imaging is ongoing.
- In some cases, we may ask the patient to move through the full range of motion for extensive visualization of the joint.
- Once the arthrogram is complete, the patient will have an MRI or CT performed immediately afterward.
How Long Does an Arthrogram Take?
The total amount of time for an arthrogram with contrast medium may range from one to two hours. After the injection has been administered, it is necessary to wait a short time before imaging can be conducted. The remainder of time depends on the type of imaging that is requested. CT scans may take less than 30 minutes, while MRI imaging may take up to 45 minutes. We suggest allotting approximately 2 hours for the entire process.
Patient Testimonial
I just wanted to thank you for my enjoyable experience at your facility. (Your staff) was wonderful at fitting me in so quickly and was very kind and personable. (The technologist) was gentle and explained everything that was going to happen. When leaving your facility I was given a thank you gift which was very classy & made me feel really good. You followed up with a thank you note which completed my process. How kind of you to treat you patients like important people. You get an A+. Thank you again for making my experience a great one.
-Candice G.
To read more, visit our testimonial page.
Does an Arthrogram Hurt?
We do everything that we can to make imaging a comfortable experience for each patient. During an Arthrogram, a patient may feel a slight sting when the doctor injects the anesthetic just beneath the skin.
When contrast material enters the joint, a sensation of fullness, discomfort, tingling, or pressure may occur. After the doctor administers the contrast media, some patients also notice a slightly salty or metallic taste for a few moments.
It is necessary to hold very still during parts of the arthrography exam. This is usually just a few seconds to a few minutes at a time. The exam may take 10-30 minutes.
Side Effects of an Arthrogram
Soreness in the joint may occur due to the injection of contrast dye. This side effect usually decreases significantly within the first two days after the arthrogram.
Arthrogram Risks
Arthrography, the process of obtaining the arthrogram image, is very safe. The most severe complication that may result from arthrography is an infection in the joint. This is a rare occurrence that happens in the specific instance that organisms are present on the skin at the time that dye is injected into the joint. Organisms may transfer into the joint at this time. Though this risk is rare (1 in 40,000), imaging that involves injection is not conducted if infection or inflammation is present.
There is also a chance that the contrast medium may cause an allergic reaction. Usually, this is nothing more than a rash. However, the allergic response may be severe in some cases. According to available data, approximately 1 in 2000 people who undergo imaging with contrast medium experience rash or hives.
Arthrogram Recovery
Results
Images obtained during the arthrogram are reviewed by one of our radiologists. Following the exam, we prepare a full report and forward it to the referring physician within a few days.
GO Imaging facilities are fully accredited by the American College of Radiology. Our board-certified radiologists and ARRT-certified radiology technologists offer exemplary service to patients and their referring physicians.

